
For thousands of years, diamonds have inspired emotions, mesmerized and seduced. The Greeks believed diamonds were the tears of the Gods while Romans theorized they were fragments of stars fallen from the sky. The Egyptians placed a diamond ring on the fourth finger, believing a ‘vein of love’ ran directly from the finger to the heart. They have been the source of endless stories and ultimately, a diamond’s beauty is the rarest of all their qualities.
Ultimately, the old adage, “beauty is the eye of the beholder,” could not be more true when it comes to selecting a diamond. The same as falling in love, diamonds have a way of attracting one with its unique sparkle or its one-of-a-kind color. However, it is important to review the basics in the guide below for some inside knowledge to make the purchase an exciting venture. Sotheby’s specialists share their 8 tips so you can buy diamonds like an expert.

FIVE UNMOUNTED DIAMONDS
1. What exactly is a carat?
The weight of a diamond is measured worldwide by a standard unit: the carat. The name “carat” comes from the seed of the carob tree native to Mediterranean regions, once used to weigh stones. A carat weighs 0.2 grams.
2. What is the GIA? What is a GIA certificate?
The GIA is the Gemological Institute of America, an independent laboratory respected worldwide. Each stone over 1 carat receives a certificate (“identity card”) attesting to the quality of the stone (4 Cs) and details its properties.
3. What do the 4 Cs stand for?
The 4 Cs are a global standard diamond certification developed by the GIA. These four criteria are colour, clarity, cut and carat, which determine the quality and therefore value of a diamond. The color scale begins with the letter D, representing colorless, and continues with increasing presence of yellow, brown or grey to the letter Z. Each letter grade has a clearly defined range of color appearance. Clarity refers to the absence of inclusions and blemishes, ranging from “Flawless” to “Included 3” for diamonds with obvious visible inclusions.
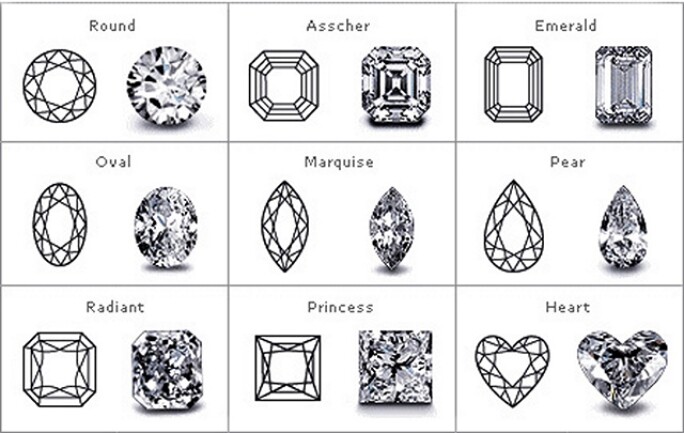

DIAMOND & GEMSTONE SHAPES.
A diamond’s cut is what unleashes its light. The GIA calculates the proportions of those facets that influence the diamond’s face-up appearance to evaluate how successfully a diamond interacts with light to create desirable visual effects . The cut scale ranges from “Excellent” to “Poor”.
4. Why does the 4 Cs color scale begin with D and not A?
Before the GIA established the 4 Cs, diamond color was graded from A-C, sometimes with grades like AA or AAA. It got confusing as there was no universal agreement. As a fresh start, the GIA began with D.
5. Why does one diamond shine more than another?
The brilliance of a diamond depends on its cut, a 4 Cs criterion. The closer the cut is to perfection, the greater the diamond’s brilliance. Different cuts also have different properties that result in different appearance. An emerald cut diamond in an ideal cut will have less sparkle versus a round or radiant ideal cut diamond.
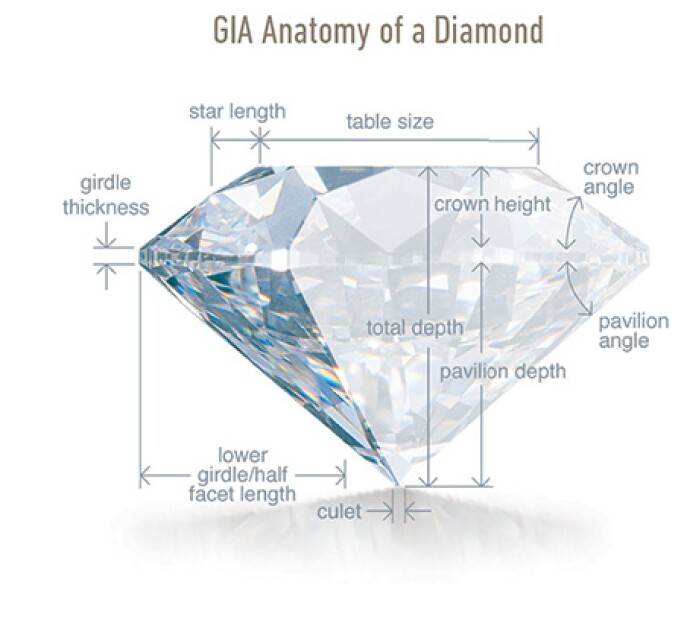
GIA ANATOMY OF A DIAMOND.
6. Can a diamond break or be damaged?
A diamond is the hardest of all gemstones and is known for its extreme durability. To contribute to its longevity, it is advisable to take great care of your diamond jewelry, preferably by keeping each diamond creation separate and avoiding contact with other pieces.
7. Why isn’t a 0.50 carat diamond half the price of a 1 carat diamond?
The price of a diamond depends primarily on its weight (carats), as larger diamonds are more rare. The price of a diamond increases exponentially. A 1 carat solitaire is therefore around four times more expensive than a 0.50 carat solitaire of equal diamond quality. The other 3 Cs also contribute to value.
8. What is the Kimberly Process?
The Kimberley Process is a joint government, international diamond industry and civil society initiative to stem the flow of diamonds used by rebel movements to finance wars against legitimate governments. These are known as “Conflict Diamonds”. The World Diamond Council System of Warranties is a programme of self-regulation that tracks diamonds through the supply chain. The System of Warranties requires all diamond suppliers and manufacturers to pass on a warranty statement, assuring any buyer of the diamond legitimacy.
Articol preluat de pe https://www.sothebys.com/en/articles/buy-diamonds-like-an-expert-with-these-8-tips
